Understanding Data Privacy in Digital Marketing
Data privacy in digital marketing involves securing personal details gathered during promotional activities, such as names, email addresses, phone numbers, location data, and browsing habits. Each piece of data can reveal intimate details about consumers, necessitating stringent protective measures.
Non-compliance with data privacy regulations exposes companies and customers to various risks, including data breaches, legal actions, and substantial fines. The impacts extend beyond immediate financial penalties, as consumer trust can deflate overnight if personal data is mismanaged. Reflecting on stats such as 87% of consumers shunning companies with poor cybersecurity showcases the central role of trust in business-consumer relationships.1
Marketers must handle these intricacies while engaging their audience effectively. This balance often involves obtaining explicit consent before data collection, clearly communicating the purpose of acquisition, and enforcing advanced security measures to shield collected data from unauthorized access.
Respecting data privacy can be a competitive advantage, allowing brands to differentiate themselves by demonstrating their commitment to consumer safety. This commitment can be decisive for consumers when choosing between brands, particularly in sectors handling sensitive information.
Marketers must continually update their knowledge and strategies in response to evolving regulations and consumer expectations regarding data privacy. Recent adjustments in legislations like GDPR and CCPA have pressed businesses worldwide to tweak their operational protocols related to customer data handling.
In sum, understanding and implementing data privacy measures is indispensable in digital marketing, safeguarding consumer details, company reputation, and operational legitimacy. Prioritizing these aspects can augment customer trust and business sustainability in the dynamic landscape of digital marketing.

Impact of Data Privacy Regulations on Marketing Strategies
The introduction of data privacy regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) has fundamentally shifted how marketers handle customer data. These regulations mandate a higher degree of transparency and consumer control over personal information.
Under GDPR, businesses must ensure explicit and informed consent before collecting personal data. Marketers must provide clear, concise statements on how a customer's data will be used and obtain unequivocal approval from the user. GDPR also imposes harsh penalties for non-compliance, with companies facing fines up to 4% of annual global turnover or €20 million. This has spurred companies to re-evaluate and reconstruct their data handling processes.
Similarly, the CCPA emphasizes giving California residents the right to know about the personal data collected on them and the purpose. It grants consumers the right to demand businesses delete their personal information. Businesses targeting Californian consumers have had to fine-tune their procedures and customer interfacing portals to facilitate these rights.
The impact of such regulations extends beyond compliance. Marketers need to embed privacy into their strategies, managing customer data as a liability requiring careful governance. The shift towards 'privacy by design' approaches means marketers must consider privacy at the initial design stages of data collection systems.
Adherence to privacy regulations often demands technology upgrades and staff training, which can increase operational costs. Digital platforms have been adjusted, and marketing teams have had to forgo some aggressive data-driven techniques that could potentially endanger user privacy.
While these regulations introduce constraints on marketing strategies, they also offer an opportunity to rebuild consumer trust by advocating transparency and respect for user privacy. Emphasis on compliance can enhance brand reputation, turning a potential obstacle into a unique selling proposition for ethical marketing practices. Staying updated and compliant with these dynamic regulations remains paramount, reflecting a proactive commitment to ethical marketing and consumer respect.
Consumer Trust and Data Privacy
Developing trust between consumers and companies is primarily hinged on sound data privacy practices. In an era where data missteps are often public and costly, ethical use of data plays a monumental role in building or degrading trust. Consumer skepticism is triggered by recurring data breaches touching on prominent corporations, highlighting the perpetual risk of data mismanagement.
When companies fail to protect data, a significant percentage of consumers would discontinue dealings with such companies and dissuade others based on poor data security. This creates a ripple effect where the reputational damage extends far beyond an immediate dip in sales, corroding long-term brand loyalty and consumer trust.
Yet, when companies adhere to robust data privacy regulations and champion transparent data practices, they cultivate a perception of respectability and responsibility. Modern consumers, especially digitized urban cohorts manifesting increasing privacy consciousness, tend to favor companies that are upfront about what data is collected and explicit about how it's used. Respect for user autonomy, letting consumers retract consent or request data deletion, also resonates strongly with customer bases keen on managing their digital footprints.
Integrating ethics into data handling positions a company as an industry leader in consumer rights protection, an image augmenting consumer confidence and potentially drawing in more business. Publicizing participation in industry watchdog groups or third-party certifications in privacy can further aid companies in distinguishing themselves amidst a crowded market where data-handling mediocrity is becoming increasingly intolerable.
The consequences of neglecting proper data privacy measures can be dire. Analysis from various markets shows a close correlation between news of data breaches and immediate stock value drops, reflecting investor apprehension about potentially cascading financial and reputational backlash. These breaches also invite legal ramifications which bring fines and constraining settlements that can hamstring a company's operations.
Effective data privacy practices are a strategic essential that nurtures customer trust. This trust translates into sustaining current customer bases and tapping into new demographics increasingly championing for responsible use of their personal information.

Technological Solutions for Data Privacy in Marketing
As marketers increasingly rely on digital platforms, the dependence on technological solutions to ensure data privacy is paramount. The armory of tools at their disposal is expansive, ranging from consent management platforms (CMPs) to advanced data encryption technologies.
Consent management platforms facilitate the collection, storage, and revocation of user consents, ensuring that all data activities stand on legal ground. Their significance was magnified with the enforcement of GDPR and CCPA, where user permission became a mandatory compliance requirement. CMPs aid marketers by seamlessly integrating these consent frameworks into various digital interfaces.
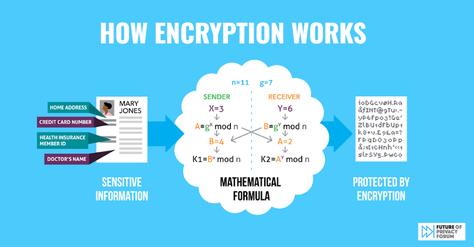
On the security front, securing data from unauthorized access has pushed companies to adopt robust encryption technologies. Encryption acts as a dual safeguard, protecting data at rest and in transit, ensuring that sensitive information is cloaked against potential breaches. Technologies like Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) encrypt the data exchanged between browsers and web servers.
Secure data storage also plays a vital role in data privacy, particularly in compliance with laws that specify data residency requirements. Solutions such as cloud storage equipped with advanced encryption standards (AES) provide marketers with secure havens for storing customer information while enabling easy access control.
Additionally, automation in data privacy has proved beneficial. Tools that employ artificial intelligence (AI) to automatically classify and tag sensitive information ensure constant surveillance and protection of personal data, reducing the human error factor significantly. These automated systems can quickly adapt to new regulatory requirements and enforce policies across massive datasets.
The complexity of data privacy laws also necessitates sophisticated Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs), performed with technological tools designed to analyze and mitigate the risks associated with data processing activities. These assessments are pivotal in identifying substantial risks and enforcing appropriate measures to mitigate them before deploying new marketing strategies.
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized approach to securing personal data. By design, blockchain can enhance transparency and provide tamper-proof mechanisms for data storage and transmission. Its application within digital marketing frameworks is being explored to empower user consent and audit trails.
The integration of these technological advances into marketing strategies assists in compliance with international data protection laws and fundamentally shifts the business culture towards prioritizing consumer privacy. As regulations continue to evolve and cybersecurity threats become more sophisticated, the role of technology in marketing as a means to safeguarding privacy becomes increasingly indispensable. Marketers must adeptly manage these technologies, harmonizing innovative digital marketing strategies with rigorous data protection mechanisms to ensure they meet legal standards and reinforce the trust of their consumers.

Future Trends in Data Privacy and Marketing
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the landscape of data privacy. With innovations rolling out rapidly, future trends point toward even more stringent requirements and sophisticated expectations from consumers regarding how their personal data is handled. Understanding and preparing for these shifts is crucial for businesses that want to stay ahead and maintain both compliance and trust.
One emerging trend is the increased demand for transparency. Consumers are steadily becoming more savvy about data privacy and want detailed disclosures about what data is collected, how it's used, and who it's shared with. To keep pace, businesses will need to invest in more robust transparency initiatives and provide clear, easy-to-understand disclosures. This could involve designing interfaces that offer real-time insights into how data is being used at any point in the customer journey.
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in marketing opens new frontiers for personalized consumer experiences but also presents significant data privacy challenges. Future regulations may require that AI systems be designed to prioritize privacy, ensuring that personal data used to train models is handled according to strict guidelines to prevent misuse. Businesses should consider adopting privacy-by-design frameworks that integrate these considerations right from the initial phases of AI model development.
Another trend likely to shape the future of data privacy in marketing is the enhancement of consumer control over their personal data. We might see a shift from the current opt-out models to more stringent opt-in models, where businesses must obtain explicit consent before any personal data collection begins. As part of this, consumer rights to modify, export, and delete their data will become more streamlined, pushing companies to implement more dynamic and responsive data management systems.
Blockchain technology could play a key role here, providing more secure and transparent ways of handling personal data by creating a decentralized record of data transactions. This could reassure consumers about the integrity of how their data is handled and ensure compliance with regulations transparently and efficiently.
With intermittent but significant amendments to data privacy laws expected across different regions, businesses operating globally will need to maintain agility in their compliance strategies. Multi-national campaigns will have to be adaptable, capable of conforming to the varying degrees of regulation evident in disparate markets. Future marketing strategies will increasingly need to be built on platforms that ensure compliance continuously, through regular updates and checks against regulatory changes worldwide.
Biometric data is also becoming a hot topic in marketing avenues with technologies like facial recognition and fingerprint identification being utilized in personalized advertisements. The ethical use and regulation of biometric data will likely see rigorous new guidelines as concerns about consent and potential misuse intensify.
In preparing for future changes in data privacy and consumer expectations, companies must look beyond mere regulatory compliance. Investing in a corporate culture that inherently respects consumer privacy and values data protection as more than just a legal obligation can set a company apart as a leader in ethical business practices. This will satisfy legal requirements and cultivate lasting trust with customers.
Professional development in data privacy for marketing teams will become crucial. Marketers will need continuous training on existing and emerging privacy regulations, equipping them to handle personal data sensitively and ethically across all marketing operations.
The future of data privacy in marketing is shaping up to be more complex and integral to a brand's reputation and consumer trust paradigm. Successfully navigating this future will require foresight, adaptability, and a steadfast commitment to ethical practices, all of which will define the next era of marketing success.

- Identity Theft Resource Center. Annual Data Breach Report 2020. 2021.


